Day: April 23, 2024
(Eurasianet) — The Russians are leaving, the Russians are leaving! That is the reality on the ground in Nagorno-Karabakh. Yet, as Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev tells it, Russian security interests in the Caucasus are not disappearing anytime soon.
Both Russian and Azerbaijani officials confirmed on April 17 that Russian peacekeepers would start withdrawing immediately, a year ahead of schedule.
About 2,000 Russian peacekeepers arrived in late 2020 after Moscow brokered a ceasefire that suspended fighting in the second Karabakh War. Those troops effectively stood aside last fall as the Azerbaijani military swept through Karabakh, reconquering all the territory lost by Baku during the first bout of fighting between Armenia and Azerbaijan in the early 1990s, and driving out over 100,000 ethnic Armenian residents of the territory.
Some political analysts believe the peacekeepers’ early withdrawal is a result of the draining effects of the Russian-Ukraine war, which, they say, has sapped the Kremlin’s strength to project influence elsewhere. In Moscow for an April 22 meeting with Russian leader Vladimir Putin, Aliyev sought to dispel any notion that Russia was quitting the Caucasus.
“Russia is a fundamental country in terms of regional security in the Caucasus and in a wider geography,” the presidential press service quoted Aliyev as saying before the start of his talks with Putin.
The failure of Russian peacekeepers to keep a lid on hostilities in Karabakh prompted a rupture in the Armenian-Russian strategic partnership. Meanwhile in Azerbaijan, the Kremlin’s checkered history in its dealings with the country causes some older Azerbaijanis to be leery of Moscow’s motives and intentions.
Since the completion of the reconquista last year, a good number of Azerbaijani citizens believe there must have been some deal between the Russian and Azerbaijani governments: Baku got a free hand in Karabakh, and in return, Moscow gets … what? The April 17 announcement did not put an end to the speculation of a quid-pro-quo. “May God make it end in peace. What did they [Russians] ask for in return? A man is afraid to even think about it,” one Facebook user commented on the news.
Baku-based analyst Shujaat Ahmadzade scoffed at what he described as a “reductionist interpretation” of Azerbaijan-Russian relations. The withdrawal of the peacekeepers could well be rooted in pragmatism, without ulterior motives. With the Russia-Ukraine war dragging on, the Kremlin can use the troops elsewhere, and will not mind the savings involved in curtailing the deployment. Besides, Ahmadzade said, the two states have lots of common interests at the moment, including a mutual desire to expand North-South trade routes.
“The situation is more nuanced,” he said, adding that the bilateral relationship “fluctuates like a rollercoaster with occasional highs and lows. Currently, there appears to be alignment between Azerbaijan and Russia on various issues.”
A sign of such alignment is the similar messaging coming out of Moscow and Baku concerning regional developments, underscored by the two countries’ criticism of recent efforts by the United States and European Union to expand economic relations with Armenia.
At their Moscow meeting, Aliyev and Putin both indicated that bilateral relations were focusing on trade more than security. Putin in his pre-meeting remarks touted the growth of bilateral trade turnover, which now exceeds $4 billion annually.
Technically, the occasion of the Aliyev-Putin meeting was to commemorate the 50th anniversary of the Baikal-Amur Railway, known as BAM. Though both Putin and Aliyev lauded BAM on April 22 (which also happened to be the 154th anniversary of Soviet founder Vladimir Lenin’s birth), the infrastructure project has had trouble fulfilling its economic promise and is largely an enduring symbol of Soviet economic dysfunction during the “stagnation era.”
Aliyev dwelled on the expanding North-South trade route – in which Azerbaijan serves as a hub for commerce connecting India, Iran and Russia – saying it had “global significance for cargo transportation and security.”
The Azerbaijani and Russian leaders apparently did discuss regional security issues, including topics that Putin described as “sensitive.” But details were scant on the substance and results of those talks.
Speaking back in Baku on April 23, Aliyev credited Azerbaijan’s strengthened relationship with Russia as enabling the earlier-than-expected withdrawal of peacekeepers.
“This [withdrawal of peacekeepers] was a joint decision, and it only strengthens our relations. It demonstrates that when countries have normal channels of communication, when they respect each other and cooperate, when they do not do anything against each other, they can find agreement on most sensitive issues,” Aliyev said.

Disturbing reports continue to emerge about mass graves in Gaza in which Palestinian victims were reportedly found stripped naked with their hands tied, prompting renewed concerns about possible war crimes amid ongoing Israeli airstrikes, the UN human rights office, OHCHR, said on Tuesday.
The development follows the recovery of hundreds of bodies “buried deep in the ground and covered with waste” over the weekend at Nasser Hospital in Khan Younis, central Gaza, and at Al-Shifa Hospital in Gaza City in the north. A total of 283 bodies were recovered at Nasser Hospital, of which 42 were identified.
“Among the deceased were allegedly older people, women and wounded, while others were found tied with their hands…tied and stripped of their clothes,” said Ravina Shamdasani, spokesperson for the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights.
Al-Shifa discovery
Citing the local health authorities in Gaza, Ms. Shamdasani added that more bodies had been found at Al-Shifa Hospital.
The large health complex was the enclave’s main tertiary facility before war erupted on 7 October. It was the focus of an Israeli military incursion to root out Hamas militants allegedly operating inside which ended at the beginning of this month. After two weeks of intense clashes, UN humanitarians assessed the site and confirmed on 5 April that Al-Shifa was “an empty shell”, with most equipment reduced to ashes.
“Reports suggest that there were 30 Palestinian bodies buried in two graves in the courtyard of Al-Shifa Hospital in Gaza City; one in front of the emergency building and the others in front of the dialysis building,” Ms. Shamdasani told journalists in Geneva.
The bodies of 12 Palestinians have now been identified from these locations at Al-Shifa, the OHCHR spokesperson continued, but identification has not yet been possible for the remaining individuals.
“There are reports that the hands of some of these bodies were also tied,” Ms. Shamdasani said, adding that there could be “many more” victims, “despite the claim by the Israeli Defense Forces to have killed 200 Palestinians during the Al-Shifa medical complex operation”.
200 days of horror
Some 200 days since intense Israeli bombardment began in response to Hamas-led terror attacks in southern Israel, UN human rights chief Volker Türk expressed his horror at the destruction of Nasser and Al-Shifa hospitals and the reported discovery of mass graves.
“The intentional killing of civilians, detainees and others who are hors de combat is a war crime,” Mr. Türk said in a call for independent investigations into the deaths.
Mounting toll
As of 22 April, more than 34,000 Palestinians have been killed in Gaza, including 14,685 children and 9,670 women, the High Commissioner’s office said, citing the enclave’s health authorities. Another 77,084 have been injured, and over 7,000 others are assumed to be under the rubble.
“Every 10 minutes a child is killed or wounded. They are protected under the laws of war, and yet they are ones who are disproportionately paying the ultimate price in this war,” said the High Commissioner.
Türk warning
The UN rights chief also reiterated his warning against a full-scale Israeli incursion of Rafah, where an estimated 1.2 million Gazans “have been forcibly cornered”.
“The world’s leaders stand united on the imperative of protecting the civilian population trapped in Rafah,” the High Commissioner said in a statement, which also condemned Israeli strikes against Rafah in recent days that mainly killed women and children.
This included an attack on an apartment building in the Tal Al Sultan area on 19 April which killed nine Palestinians “including six children and two women”, along with a strike on As Shabora Camp in Rafah a day later that reportedly left four dead, including a girl and a pregnant woman.
“The latest images of a premature child taken from the womb of her dying mother, of the adjacent two houses where 15 children and five women were killed, this is beyond warfare,” said Mr. Türk.
The High Commissioner decried the “unspeakable suffering” caused by months of warfare and appealed once again for “the resulting misery and destruction, starvation and disease and the risk of wider conflict” to end.
Mr. Türk also reiterated his call for an immediate ceasefire, the release of all remaining hostages taken from Israel and those held in arbitrary detention and the unfettered flow of humanitarian aid.
Massive settler attacks in West Bank
Turning to the West Bank, the UN rights chief said that grave human rights violations had continued there “unabated”.
This was despite international condemnation of “massive settler attacks” between 12 and 14 April “that had been facilitated by the Israeli Security Forces (ISF)”.
Settler violence has been organized “with the support, protection, and participation of the ISF”, Mr. Türk insisted, before describing a 50-hour long operation into Nur Shams refugee camp and Tulkarem city starting on 18 April.
“The ISF deployed ground troops, bulldozers and drones and sealed the camp. Fourteen Palestinians were killed, three of them children,” the UN rights chief said, noting that 10 ISF members had been injured.
In a statement, Mr. Türk also highlighted reports that several Palestinians had been unlawfully killed in the Nur Shams operation “and that the ISF used unarmed Palestinians to shield their forces from attack and killed others in apparent extrajudicial executions”.
Dozens were reportedly detained and ill-treated while the ISF “inflicted unprecedented and apparently wanton destruction on the camp and its infrastructure”, the High Commissioner said.

By Connor Fiddler
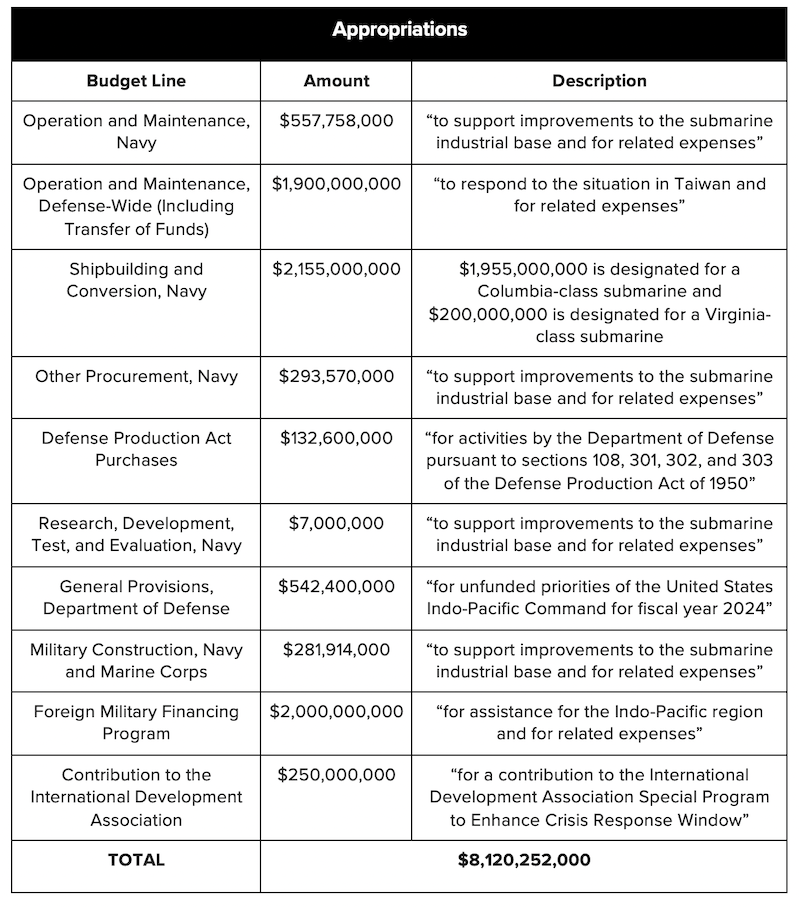
(FPRI) — In October 2023, the White House requested emergency supplemental appropriations for Fiscal Year 2024 to provide additional aid to Ukraine, Israel, and the Indo-Pacific. After months of debate, the House of Representatives passed an emergency $8.1 billion supplemental appropriations bill to support Indo-Pacific priorities. The content is very similar to the Senate version, and President Joe Biden has stated that he supports the bill. While media reports have labeled this bill as Taiwan aid, the actual provisions have a much more significant impact beyond Taiwan.
Submarine Industrial Base
For decades, American naval shipbuilding has stagnated. According to a new report commissioned by Secretary of the Navy Del Toro, the Navy faces years of delays for several major shipbuilding projects. Defense budget cuts, skilled-labor shortages, confusing demand signals, and supply chain challenges have all contributed to the crisis. Submarine shipbuilding has particularly suffered. The United States has recently produced 1.2 Virginia-class submarines a year, well below the required production rate of two a year. The White House’s plan to sell three to five submarines to Australia under the AUKUS trilateral has increased concerns about domestic shipbuilding capacity and fleet size. Using the White House’s request as a guide, the House emergency supplemental addresses some lingering concerns about maritime infrastructure.
In total, $3.3 billion has been appropriated to support the submarine industrial base. While this investment will certainly bolster deterrence in the Indo-Pacific, it will have a much more immediate impact on American jobs. $1.9 billion was designated for the construction of a Columbia-class submarine and $200 million for a Virginia-class submarine. The vast majority of this money will be spent in the United States. Groton, Connecticut and Newport News, Virginia are the two largest submarine shipyards and will benefit from this influx of cash. However, Groton and Newport News will not be the only beneficiaries. More than 16,000 suppliers across all 50 states contribute to the submarine industrial base and will benefit from this new appropriation. Additionally, $7 million was appropriated for research and development, supporting numerous laboratories and research facilities.
Nearly half of the Indo-Pacific appropriations directly reinforce the submarine industrial base. While this investment will enhance deterrence in the Indo-Pacific, the immediate impact will be supporting the American economy.
Talking Tough and Doing Tough
One of the most significant line items is $2 billion in Foreign Military Financing (FMF) “for assistance for the Indo-Pacific region and for related expenses.” Despite many in Washington raising concerns about Chinese coercion toward Taiwan, only recently has Congress taken commensurate actions to support Taiwan.
FMF aid is a critical tool for supporting American allies and partners. FMF allows designated nations “to purchase US defense articles, services, and training through either foreign military sales or, for a limited number of countries, through the foreign military financing of direct commercial contracts program.” The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2023 was the first time Congress authorized the provision of FMF for Taiwan: up to $2 billion a year in direct loans and loan guarantees and up to $2 billion a year in grant assistance through FY2027. However, the grant assistance was not appropriated. In June 2023, the Biden Administration approved FMF assistance for the first time to Taiwan. It remains unclear if the Biden Administration will use all $2 billion appropriated.
Looking Ahead
As US military support for Ukraine has starkly shown, the US defense industrial base has atrophied over the years. Fixing these issues now is preferable to doing so during a contingency. The considerable investment in the submarine industrial base is promising. Additionally, the $2 billion allocation of FMF to Taiwan indicates that Congress is getting more serious about supporting Taiwan’s defense. Washington must build off this supplemental. In general, military shipbuilding remains slow and insufficient. While FMF loans are helpful, appropriators should allow for FMF grants to better bolster Taiwan’s military. The passing of this emergency supplemental is a much-needed victory.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and do not necessarily reflect the position of the Foreign Policy Research Institute, a non-partisan organization that seeks to publish well-argued, policy-oriented articles on American foreign policy and national security priorities.
- About the author: Connor Fiddler is the Associate Deputy Director for the Asia Program at the Foreign Policy Research Institute.
- Source: This article was published by FPRI
By Natalie Tavadze
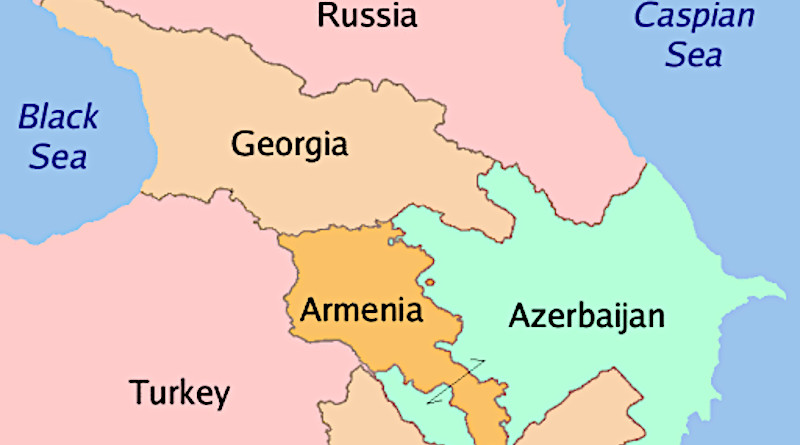
For years, to avoid the confusion between Georgia the country, and Georgia the U.S. state, international media referred to the former as a post-Soviet entity. It seemed that only in the wake of the 2008 Georgian-Russian war (when Americans were finally assured that it was not their state being attacked) did the country rise to global attention. Nowadays, it appears that Georgia, next to its immediate neighbors Armenia and Azerbaijan (together forming the Central Caucasus), draws attention due to its role in the so-called Middle Corridor (TITR). However, it eluded the attention of many that the area has long obtained three distinctive geopolitical roles owing to its location. These were: a bridge of economic interactions, a buffer between Europe, Russia, and the Middle East, and a border of different civilizations.
There were reasons why it evaded the notice of many, but first and foremost, we should mentally map the area. The Central Caucasus, comprised of Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan, is a historically constructed, complex political concord, embodying a geopolitical tapestry woven over centuries and forming a culturally, ethnically, linguistically, and religiously diverse area stretched between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea.
In the geopolitical discourse, as explained by Saul Bernard Cohen, an eminent American geographer, the axiom stands firm: “Geopolitics is a product of its time.” Each historical period has produced a geopolitical model offering a lens through which to interpret the world map and the world order of that time. In imperialist geopolitical writings of the 19th to early 20th centuries when a state’s greatness lay in its maritime power and/or in domination of the Heartland (the territory ruled by the Russian Empire and later by the Soviet Union), the distance of the Central Caucasus from the Anglo-American space resulted in little to no mention of the region.
Whilst the strategic location of the Central Caucasus temporally escaped the attention of imperialist writers, historically, the region carried geopolitical importance for three major Eastern powers: The Persian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian Empire. Already in the early 1800s, the region acted as a buffer zone between Orthodox Christianity and the Muslims of the Middle East. Russia’s expansion into the Caucasus in the sixteenth century additionally carried economic considerations, evident in projects like the Trans-Caspian railway, which facilitated access to Central Asia and control over Caspian oil supplies. Next to its geographical advantages, the Central Caucasus was a boon for natural resources. Besides Petroleum, the region is rich in copper ore. The minerals also attracted foreign investors and as of 1870, Rothschild and Shell was extracting oil, while Siemens mined copper.
After World War II, the political picture drastically changed and a new international system emerged, with multipolarity giving way to bipolarity. During the Cold War, geopolitics became associated with the two leading ideologies of that time: Communism and Western Democracy. Geopoliticians, thus, were mostly preoccupied with the rivalry between the two blocs of the West and the East. When the Soviet Union established its rule over the Central Caucasian states, the region once again became extraneous to the interests of international observers and witnessed its geopolitical role as a bridge for regional and international trade routes reduced to serving the southeastern border of Europe with Communist Russia and the Middle East.
By the 1980s, however, “winds of change” were blowing on the Eastern side of the Iron Curtain, and with Mikhail Gorbachov’s policies of glasnost and perestroika, the Cold War was nearing its logical end, giving way to a new world order. Simultaneously, geopolitical concepts were updated to understand the new world map and where geopolitical pivots had moved, which came to be known as the New World Order in an academic context. While some rejoiced in triumph of the Western ideology and others coined a neologism “Geo-economics” to explain the substantial penetration of economics into geopolitics, a drastically different approach was undertaken by Samuel P. Huntington to explain the geopolitical setting and patterns of this “new world.” He emphasized cultural differences as the primary basis for identity and conflict, predicting that nations would align along cultural lines rather than ideological or economic ones, leading to conflicts at local and global levels. Huntington identified several fault lines, including the Balkans, the Caucasus, and the Middle East, as areas where clashes between civilizations were likely.
Now, in addition to its geographically determined strategic function as a buffer and bridge on two axes – West-East and North-South, the region’s ethnoreligious mosaic was also put under the spotlight of geopolitical works and international actors. Geographically situated between Orthodox and Islamic civilizations, the region has fostered a diverse ethno-religious mosaic. Despite religious differences, examples of religious tolerance can be found in cities like Derbent, Dagestan, and Tbilisi, Georgia. Additional emphasis is given to the role of customs, which in the Caucasus is referred to as ‘adat.’ It is argued that customs (or adats) in the region are stronger than confessions, and even contend for superiority over the latter. The custom-based relationship between the peoples of religion facilitated their peaceful coexistence, tolerance, and mutual understanding. The historical background of peaceful coexistence and distinct patterns of Caucasian, custom-based relations between different religions and ethnicities, provided the understanding behind the harmonious relationship between the Caucasian people.
The Russian Effect
The demise of the Soviet Union, however, did not mean the end of the Cold War rationale. Russia – as the heir of the Soviet Union – after disappointing the hopes of anticipated democratization was still considered a power whose influence had to be contained. Zbigniew Brzezinski, like many of his contemporaries and those before him, assumed that Russia at some point in post-Cold War history, whether voluntarily or not, would choose the path of Western development, a hope that remains unrealized to this day. The reasons behind this can be traced back to the Russian understanding of the world system, which has been incautiously neglected by Western academia and which is vividly illustrated by the Russian geopolitical school: Eurasianism. All important contributors to the development of Russian Geopolitics (Nikolai Trubetzkoy, Peter Savitsky, Lev Gumilev, Aleksandr Dugin) emphasized Eurasia’s distinct cultural-geographic and socio-historical pattern and rejected Western universal ideas of the cultural and historic development of mankind. It was believed that it was Russia’s mission to unify Eurasia and maintain this unity, asserting that it was the destiny of the Eurasian people to be concerted.
It is important to understand that Eurasianinism and Moscow’s approaches toward the Caucasus correspond to each other. In this regard, the Central Caucasus is considered as Russia’s backyard. Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Armenia, the Black Sea, and the Caspian Sea constitute strategic dimensions for Russia. The latter is determined to dominate the region and uses the “ethnic card” to keep the countries of the Central Caucasus off balance. From the Russian standpoint, any foreign influence in its “near abroad” is seen through the prism of its national security. Such a menace should be thwarted by any means, as Moscow made clear more than once that it does not entertain any notion of conceding territories of its utmost geopolitical interests.
As the successor of the Soviet Union, Russia experienced the heaviest losses in terms of territory, resources, influence, economy, as well as international image. Its borders were pushed back from the west, south, and east. To add fuel to the fire, the divorce of the Central Caucasian states from Russian influence and the emergence of newly independent states in Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan with nationalist-minded political elites reinforced the fears of a resurgence of the deep-rooted Russian-Turkish rivalry over influence in the region. A prominent Eurasianist Alexandr S. Panarin argued, that “the geopolitical concessions which post-Soviet Russia made to the West are the maximum Russia will ever concede. Any further attack by the West Belt in the form of further enlargement of NATO or by playing the Ukrainian, Georgian, Azeri, or Central Asian ‘cards’ would mean that the aforementioned concessions by Russia were like the concessions to Hitler at Munich.”
Dominating the Caucasus for Russia also translates into being closer to the Mediterranean and Balkans. Some of the imperialist-minded politicians, such as Vladimir Zhirinovsky, expressed the ambition of obtaining access to a warm water port on the Indian Ocean. Needless to say, conceding the vital Caspian Sea resources it could potentially lose with the opening of the market to the west – along with flows of Western investment following the breakup of the USSR – would substantially weaken Russia.
The Caucasian Chalk Circle
In the context of the so-called emerging New World Order, Russia was at first left on the periphery, while Turkey and Iran were the first countries affected by geopolitical turbulence. Entering the ‘Mittlespiel’ of this ‘Great Chess Game,’ the United States and the European Union quickly exploited the opportunity to increase their influence in the region of the Central Caucasus. Hence the latter soon became a space of competition between original geopolitical players and so-called ‘newcomers.
Iran is one of the classical players in the Central Caucasus, however, due to its internal turbulence and international pressures, it was forced to temporarily retreat from the contest. The latest trends show the revitalization of Iran’s interests in the Central Caucasus. In the regional context, Iran is an ally of Armenia and Russia.
Turkey, as Brzezinski suggests, must not be alienated from geopolitical calculations, because a rejected Turkey can not only become strongly Islamic but will be able to upset the region’s stability. Turkey’s role in this contest, along with its geopolitical inclinations, is to counter-balance Russia’s domination over the region. That is why Brzezinski argues that political developments in Turkey and its orientation will be crucial for the states of the Central Caucasus.
The EU presence in the region is perceptible as well. In the framework of its Eastern Neighborhood Partnership, the Union encouraged countries of the region toward reform and as an accolade granted Georgia candidacy status. Furthermore, the location and the mentioned potential to provide transit roads allow Central Caucasus to serve as an energy security guarantee to Europe. In line with this, Europe needs to assist the region in its peaceful development and assure its security as a strategic partner.
Contrary to Armenia and Georgia, Azerbaijan does not openly express willingness to join either military or economic blocs. The country is neither pro-Russian, nor pro-Western, but emphasizes the importance of regional cooperation. Consequently, the countries are at different steps in the process of Europeanization. Nevertheless, the EU’s need for a reliable partner in the Central Caucasus is currently at odds with Turkey’s estrangement from the Union and Russia being non-responsive to sanctions.
The United States has long viewed the region, and especially Georgia as a strategic buffer zone to assist its interests in the Middle East, as well as against the expansion of terrorism. In 2016, Donald Rumsfeld, former US Secretary of Defense, highlighted the strategic location of Georgia in his article in The Wall Street Journal, by stating that “[Georgia] provides a barrier to the flow of jihadists from other parts of the former Soviet Union to the Middle East. And it will doubtless figure large in the strategies of any NATO consortium for securing the Black Sea and ‘New Europe’ against Russian adventurism.”
An additional newcomer to the regional chess game is China with its growing geopolitical influence, making the region’s importance even greater through participation in the Chinese Silk Road project and, since 2017, in the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route project.
The cultural dimension, specifically the ethno-religious factor, in a time of growing resurgence of nationalism and fundamentalism, is a factor directly influencing geopolitical considerations. Historical differences have shaped difficult relations between Turkey-Armenia and Armenia-Azerbaijan, leading to friendship between Russia and Armenia. Russia’s betrayal and mistreatment of Georgia has alienated the country from its northern neighbor, with whom it shares a common religion. Despite diverse religions, Georgia maintains a friendly relationship with Turkey and Iran, with the latter enjoying a somewhat positive attitude among all the Caucasian republics.
Its location and its experience as a borderland of various religions and ethnicities permit the region to be crucial in what is claimed to be the primary menace and security challenges of the 21st century- terrorism, further enhancing the Central Caucasus’s role as a border of civilizations.
As observed, the developments of the post-Soviet era brought new actors such as the US, EU, and China into the contest of imposing influence over the region, as well as extracting benefits from it. Such unfolding of events, however, runs contrary to the aspirations of the major neighboring geopolitical powers, such as Russia, Turkey, and Iran; the concentration of political interests of the great powers in such a small region emphasizes its favored geopolitical position and economic advantages.
Borrowing from Bertolt Brecht’s theatrical play The Caucasian Chalk Circle, the configuration of international interests in the region spotlights power conflicts. Such concentration of global powers in its turn shapes the foreign orientations of the countries of the Central Caucasus. In the realm of geopolitical discourse, a region can be geopolitically significant if it serves the geopolitical and economic benefits of major geopolitical players or has the potential to challenge such political-economic aspirations of great powers. The Central Caucasus, as a result of its strategic location and diversity, possesses both characteristics. Consequently, Central Caucasus stands amid a complex geopolitical landscape, and next to presenting economic opportunities for great powers, finds itself in the hotspot of 21st-century security considerations.

Mr. Narendra Damodardas Modi, serving as the 14th Prime Minister of India, has successfully completed two terms in office and is now seeking re-election for a third term in the forthcoming 18th Lok Sabha elections. Widely recognised as a prominent figure in Hindutva politics, Modi is often viewed as the face of a political ideology marked by division and animosity. Throughout his tenure, Modi has been disseminating misleading information to sway public opinion in his favour. One of the most contentious aspects of his leadership has been his portrayal of Indian Muslims as outsiders or “intruders.” This rhetoric not only underscores his divisive approach but also exacerbates religious tensions, leading to increased polarisation and communal strife in the country. Such divisive tactics not only undermine the unity of India but also pose a threat to its secular fabric and citizenship rights.
Modi’s policies and governance have often been evident for marginalising minorities, lower castes, and the working classes. This marginalisation can be traced back to the core principles of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), which is deeply influenced by the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), an organisation espousing a racist Eurocentric ideology. The RSS’s emphasis on cultural nationalism and its hierarchical view of society have shaped the BJP’s approach, leading to policies that often neglect the rights and welfare of marginalised communities.
Modi’s past remarks about Indian Muslims, first likening them to “puppies” and now branding them as “intruders,” offer a telling insight into the nature of Hindutva politics rather than merely reflecting on Modi’s personal beliefs. These comments indicate a troubling tendency to overlook and undermine the secular and inclusive principles that are at the heart of India’s Constitution.
Indian Muslims have been an integral part of the country’s fabric, actively participating in its democratic processes and contributing significantly to its growth and progress. They have made invaluable contributions across various fields such as social work, science, education, history, culture, religion, language, and literature. Their role in India’s anti-colonial struggles and nation-building efforts has been substantial, often involving sacrifices that have helped shape the nation’s identity, ethos and destiny. Hindutva political forces collaborated with British colonialism in their aim to create a Hindu Rashtra. In contrast, anti-colonial Muslim leaders not only participated and sacrificed their lives but also helped shape India’s secular and scientific ethos as a modern constitutional democracy.
By branding Indian Muslims as “intruders,” Mr. Modi not only undermines the sanctity of the Indian Constitution but also negates the rich tapestry of contributions that Muslims have made to India’s diverse heritage. Such rhetoric not only threatens to erode the concept of Indian citizenship but also perpetuates a divisive narrative that undermines national unity. Moreover, Modi’s statements are deeply offensive to all Indians who uphold the principles of equality, secularism, and the rights enshrined in the Constitution. Modi and his Hindutva forces send a message that contradicts the inclusive vision of India as a pluralistic society where every citizen, regardless of their religious or cultural background, has an equal stake and contribution to make in the deepening of Indian democracy. Muslims are as much shareholders of Indian democracy as any other citizens of India.
In essence, Mr. Modi’s remarks reflect a broader Hindutva challenge to India’s foundational values and principles. The Hindutva ideology is a foreign import that has intruded into the fabric of Indian politics, society, and culture. While claiming to represent authentic Indian values, its ethnonationalistic tendencies and focus on religious and ethnic identity have more in common with European ideologies than with India’s rich and diverse history, society, and culture. Rather than drawing from India’s pluralistic traditions and composite culture, Hindutva’s roots can be traced back to European concepts of ethnonationalism, religious nationalism and racialised democracy. This imported ideology of Hindutva politics has sought to redefine Indian pluralistic identity in narrow, exclusionary terms, often at the expense of religious and cultural minorities.
Historically, there are parallels between Hindutva and the ideologies that emerged in Europe during the early 20th century. One of the most striking comparisons can be drawn with Nazi Germany, where ethnonationalism and religious intolerance were central tenets of the regime. The ideology of Adolf Hitler, with its emphasis on racial purity, scapegoating of minorities, and use of fear and hatred to mobilise the masses, seems to provide a blueprint for Hindutva political practices in India. In both cases, fear and hatred are employed as powerful tools to manipulate public opinion and garner electoral support. The Hindutva ideology can be seen as a true intruder in Indian politics, society, and culture, drawing inspiration from European ethnonationalism rather than India’s own rich traditions. Its reliance on fear, hatred, and divisive tactics undermines the principles of secularism, pluralism, and unity that are integral to India’s democratic ethos.
By stoking communal tensions and promoting a divisive agenda, Hindutva politicians seek to consolidate their power base and rally support among certain segments of the population. This approach not only undermines India’s secular and democratic principles but also threatens to unravel the country’s social fabric by fostering mistrust and animosity among its diverse communities. It’s crucial to recognise that such divisive ideologies are antithetical to the pluralistic ethos that has been a hallmark of Indian civilisation for centuries. India’s strength lies in its diversity, and any attempt to impose a monolithic vision of identity runs counter to the country’s democratic values and inclusive heritage.
The tactics employed by Hindutva politics, including its anti-Muslim propaganda and diversionary strategies, serve multiple purposes for its proponents. First, these tactics serve to distract from the ideological shortcomings and lack of substantive policy achievements within the Hindutva framework. By focusing public attention on divisive issues and fostering communal tensions, Hindutva leaders like Mr Modi can deflect scrutiny from their governance failures and policy inadequacies. Secondly, by creating a climate of fear and suspicion, Hindutva politics seeks to consolidate its voter base by appealing to religious and ethnic identities. This strategy aims to rally support among certain segments of the population by portraying minorities, particularly Muslims, as the ‘other’ or as threats to national identity and security.
However, in the long run, such divisive politics by Hindutva forces have detrimental effects on both India and its people. Firstly, it undermines the social fabric of the country by fostering mistrust and animosity among its diverse communities. India’s strength has always been its pluralistic ethos, which celebrates its rich cultural, linguistic, and religious diversity. Hindutva’s divisive agenda threatens to erode this diversity by promoting a narrow and exclusionary vision of Indian identity. Secondly, the focus on divisive issues and religious polarisation detracts from addressing the real challenges facing the country, such as economic development, social inequality, and progressive governance reforms. By prioritising dominant identity politics over issues that affect the daily lives of ordinary citizens, Hindutva politics hampers India’s progress and development. Lastly, the international perception of India as a secular and democratic nation is also at risk due to Hindutva’s divisive agenda.
Therefore, Hindutva politics may offer short-term electoral gains by exploiting religious and ethnic divisions, its long-term consequences are detrimental to India’s unity, progress, and international standing. By prioritising divisive tactics over inclusive governance, Hindutva weakens the fabric of Indian society and undermines the democratic values that are integral to India’s identity. Mr. Modi’s bid for a third term is a continuation of his divisive Hindutva politics, characterised by misinformation, religious polarisation, and marginalisation of vulnerable groups. His leadership style and policies reflect the broader ideological framework of the BJP, influenced by the RSS’s racist Eurocentric worldview, which prioritises certain segments of society at the expense of others.
The 18th Lok Sabha elections in India present an opportunity to mend the fractured republic led by the Hindutva figurehead, Modi. The crisis facing Indian democracy under Hindutva politics highlights the urgent need for political transformation to uphold the principles of secularism and inclusivity that are fundamental to India’s democratic values. Instead of employing divisive tactics that marginalise communities based on religion or ethnicity, it’s crucial to nurture unity. It is time to defeat Modi, BJP, and RSS to steer India away from a destructive path politically, socially, culturally, religiously, and economically. Progress and prosperity in India depend on secular solidarity.